-
- Trading Platforms
- PU Prime App
- MetaTrader 5
- MetaTrader 4
- PU Copy Trading
- Web Trader
- PU Social
-
- Trading Conditions
- Account Types
- Spreads, Costs & Swaps
- Deposits & Withdrawals
- Fee & Charges
- Trading Hours

Pair trading is a market-neutral strategy that involves taking long and short positions in two historically correlated assets.
The aim is to profit from temporary divergences in their price relationship, regardless of overall market direction.
Commonly used in equities, forex, and commodities, pair trading relies on statistical analysis and technical indicators such as correlation coefficients, moving averages, and Bollinger Bands.
The strategy is designed to reduce exposure to market-wide volatility, but it requires careful monitoring, risk controls, and real-time validation of asset relationships.
Key points:
Pair trading is a market-neutral strategy that involves opening both a long and a short position in two historically correlated assets.
These assets often come from the same sector or asset class and tend to move in a similar direction over time.
By taking opposite positions in each asset, the strategy seeks to benefit from price divergence while limiting exposure to broader market trends.
The goal of pair trading is to identify when the price relationship between two correlated assets temporarily breaks down.
Traders go long on the undervalued asset and short on the overvalued one, with the expectation that their prices will revert to their historical norm.
Because gains and losses are tied to the relative performance of the two positions, this approach can help reduce directional market risk.
While pair trading can offer useful risk management benefits, it requires careful statistical analysis, historical data, and active monitoring.
Not all assets exhibit reliable correlations, and pricing relationships can shift over time.
When applied with discipline, pair trading can provide opportunities in both rising and falling markets by focusing on relative value rather than overall market direction.
Pair trading focuses on the relationship between two correlated assets, aiming to profit from temporary divergences in their price movements.
This market-neutral strategy relies on mean reversion rather than predicting market direction.
Step 1: Identify Correlated Assets
The first step is to find two assets that have historically moved in tandem.
These often come from the same sector or asset class, such as energy stocks or currency pairs, and respond similarly to external market conditions.
Step 2: Monitor Price Divergence
Traders measure the price difference between the two assets, known as the spread.
When this spread widens beyond a normal range, it may signal a temporary imbalance.
This could present an opportunity to initiate a trade.
Step 3: Enter Long and Short Positions
A typical pair trade involves buying (going long on) the undervalued asset and selling (going short on) the overvalued one.
The goal is to profit if the spread narrows again and the price relationship reverts to its historical average.
Step 4: Focus on Relative Performance
Rather than relying on the broader market trend, pair trading targets the relative movement between the two assets.
This can help reduce exposure to general market volatility while still allowing for profit opportunities.
Key Takeaways
Pair trading is based on a strong historical correlation between two assets.
Traders look for a price spread that deviates from the norm.
The strategy involves a long position on the undervalued asset and a short position on the overvalued one.
Profit potential comes from the expectation of price reversion.
The approach is market-neutral, focusing on asset relationships rather than overall trends.
Successful pair trading relies on identifying asset pairs with a strong historical relationship and monitoring when that relationship changes.
Traders use several tools to assess correlation strength and spot potential trade setups.
The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure that indicates how closely two assets move in relation to one another.
It ranges from -1 to 1:
Pairs with a coefficient above 0.8 are often considered strongly correlated.
However, this should be evaluated alongside other factors such as market conditions and timeframes.
Traders often use moving averages to track the spread between two assets over time.
These averages help visualise how closely the pair moves and can highlight moments when the spread deviates from historical norms.
A significant and unexpected shift may indicate a potential entry point for a pair trade.
Bollinger Bands are volatility-based indicators that help determine whether the price spread between two assets has moved outside its typical range.
If the spread touches or exceeds the upper or lower band, it may suggest the assets are overextended relative to their historical relationship.
This can signal a possible reversion opportunity.
Indicators for Pair Trading
| Indicator | Purpose | What It Shows | How It’s Used in Pair Trading |
| Correlation Coefficient | Measures how closely two assets move together | Value from -1 to 1; higher values indicate stronger linkage | Used to identify strong historical relationships |
| Moving Averages | Smooths price data over time | Trend direction and average spread between asset prices | Detects deviations from typical spread behaviour |
| Bollinger Bands | Measures price volatility | Spread exceeding upper/lower bands signals potential setup | Identifies when the spread may be overextended historically |
Key Takeaways
Correlation coefficients help identify strong relationships between asset pairs.
Moving averages track price spread behaviour over time.
Bollinger Bands highlight extreme deviations in the spread.
Using multiple indicators together can improve decision-making and reduce reliance on a single signal.
Applying a pair trading strategy involves a structured approach.
Data analysis, clear risk parameters, and regular performance reviews should back each stage.
Step 1: Identify a Correlated Pair
Start by screening potential asset pairs, ideally from the same sector or asset class.
Use historical data to calculate the correlation coefficient.
A value above 0.8 may indicate a strong relationship, but it is important to check that the correlation holds across different timeframes and market conditions.
Step 2: Analyse the Spread
Once a suitable pair is identified, monitor the price spread between the two assets.
Use indicators such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands to detect deviations from the historical range. This helps pinpoint potential entry points.
Step 3: Execute the Trade
Enter a long position in the asset that appears undervalued and a short position in the asset that seems to be overvalued.
The trade should remain market-neutral, meaning it is structured to benefit from relative price movement rather than market direction.
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust
Establish exit criteria before opening the trade.
This could include a return to the average spread, a time-based limit, or a maximum acceptable loss.
Monitor external events such as economic releases or geopolitical developments, as these can affect correlation stability.
Be prepared to adjust or close the position if conditions change.
Key Takeaways
Use historical data to identify asset pairs with strong, stable correlations.
Confirm trading signals with multiple indicators.
Focus on relative value, not overall market direction.
Define exit strategies in advance to manage risk.
Monitor both the trade and external factors that could influence asset behaviour.
Pair trading is a market-neutral strategy that offers several advantages, especially for traders seeking relative value opportunities while managing risk.
Below are the primary benefits.
Pair trading helps reduce exposure to broader market trends by focusing on the price relationship between two assets.
The long-short structure means traders are less dependent on whether the market as a whole is rising or falling.
Because gains on one position can help offset losses on the other, pair trading introduces a natural hedge.
This structure can reduce the impact of unexpected price swings and help stabilise returns during periods of uncertainty.
The strategy is designed to generate opportunities regardless of market direction.
Whether the broader market is trending upwards, downwards, or moving sideways, traders focus on divergences in the price relationship between the two assets.
Pair trading can be adapted to different timeframes and asset classes, including equities, forex, and commodities.
Traders can adjust their approach based on volatility levels, sector-specific developments, or macroeconomic conditions.
Key Takeaways
Pair trading lowers reliance on broad market trends through its market-neutral design.
Built-in hedging can reduce portfolio risk during volatility.
The strategy may uncover opportunities in trending or range-bound markets.
Its flexible structure allows application across various instruments and timeframes.
While pair trading can offer risk-reducing features, it also carries specific challenges that traders should be aware of before implementing the strategy.
Historical correlation between two assets does not guarantee future alignment.
Market conditions, company fundamentals, or macroeconomic trends may change, causing previously correlated assets to move independently.
Relying solely on past data without understanding the underlying drivers of the relationship can increase the risk of unexpected outcomes.
Pair trading assumes that the price spread between two assets will revert to its historical average. However, in some cases, the spread may continue to widen instead of narrowing.
This could be due to shifts in market sentiment, breaking news, or broader economic disruptions.
When convergence fails to occur, losses can affect both sides of the trade.
Many correlated asset pairs come from the same sector or industry.
While this can support the correlation, it may also expose both positions to the same underlying risks.
For example, if regulatory changes or supply chain issues affect an entire sector, both the long and short positions could experience losses simultaneously.
Pair trading is not a set-and-forget strategy. It requires ongoing monitoring, regular correlation checks, and responsiveness to market news.
Failure to adapt the trade as new data emerges can increase exposure and reduce effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
Past correlation does not guarantee future price alignment.
Price divergence can persist longer than expected, affecting both positions.
Sector-specific risks may impact both assets in the pair.
Active monitoring and timely adjustments are essential for risk control.
Pair trading strategies are often applied to assets with similar economic drivers or market behaviours.
Below are examples of commonly observed correlated pairs used in historical or theoretical trading setups.
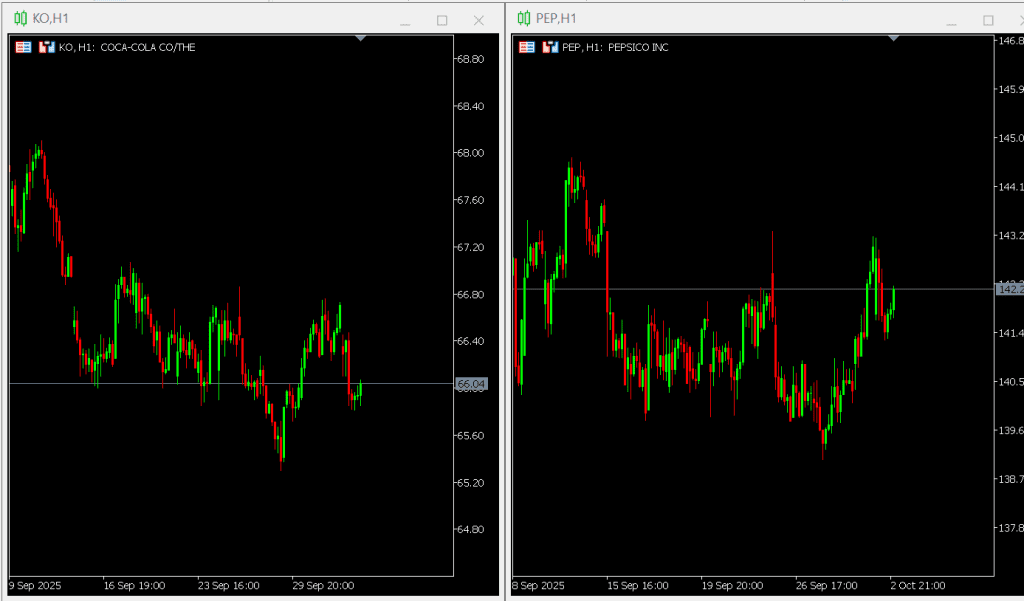
Coca-Cola and PepsiCo operate in the same industry and serve similar markets, leading to comparable stock performance over time.
Their strong historical correlation has made them a well-known example of a potential equity pair trade, where traders monitor relative valuation shifts to identify long and short opportunities.
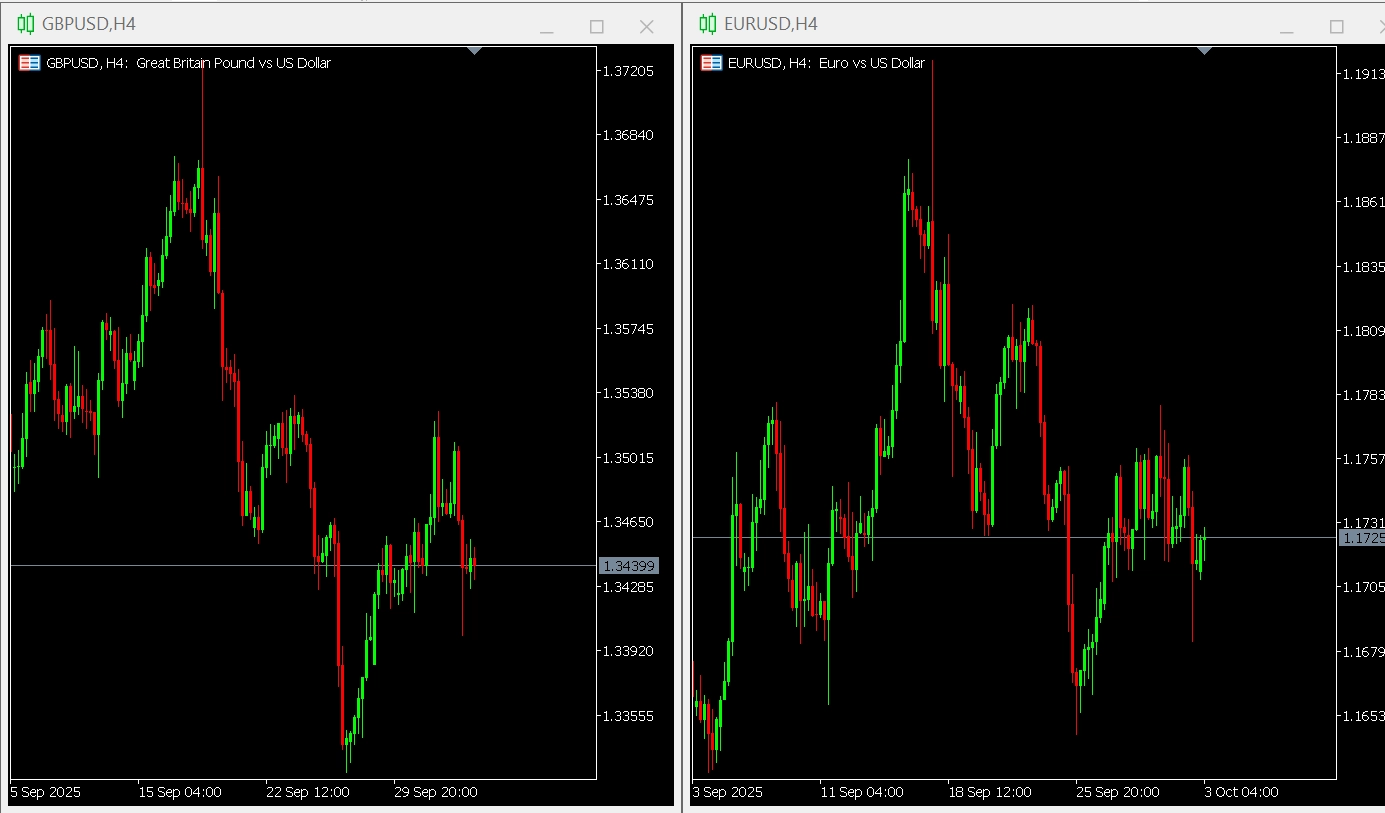
The EUR/USD and GBP/USD currency pairs both include the US dollar and are influenced by macroeconomic trends in Europe and the United States.
Due to shared economic links and overlapping trading sessions, these pairs often move in tandem.
Traders may analyse divergences in performance between the two to identify relative strength or weakness.
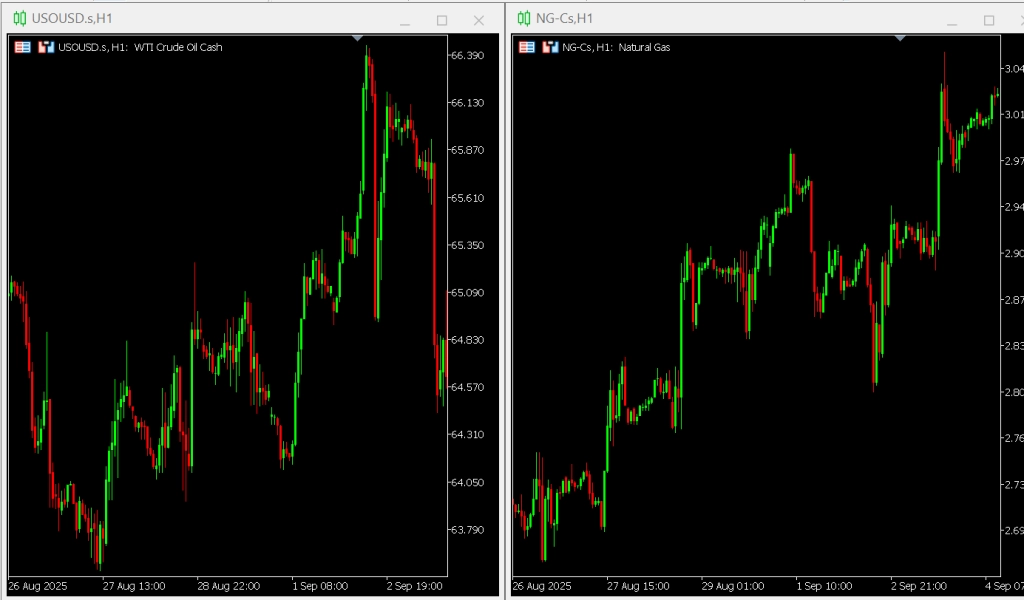
Similar global factors, including geopolitical tensions, supply and demand dynamics, and seasonal trends, shape oil and natural gas prices.
While they do not always move in lockstep, their price movements are often correlated.
Traders may track spread behaviour between the two to explore relative value setups.
Key Takeaways
Historical examples include KO/PEP, EUR/USD vs GBP/USD, and oil vs natural gas.
Each pair shares similar market drivers or sector dynamics.
Asset correlations can change over time, so analysis must be ongoing.
These examples are for illustrative purposes and should not be viewed as recommendations.
To implement a pair trading strategy effectively, traders need access to platforms that support advanced charting tools, custom indicators, and reliable execution.
Several trading platforms offer the functionality required to analyse correlations, monitor spreads, and manage open positions.
MetaTrader is widely used in forex and CFD trading for its flexibility, customisability, and support for automated strategies.
Traders can install correlation indicators, visualise price spreads, and use tools such as moving averages and Bollinger Bands.
Both MT4 and MT5 are supported by PU Prime, giving traders access to powerful tools combined with fast execution and a user-friendly interface.
PU Prime offers access to a wide range of CFDs across asset classes, including forex, indices, commodities, and more.
Traders can choose from MT4, MT5, WebTrader, or the proprietary PU Prime App, depending on their preferred trading environment.
With competitive spreads, multiple account types, and risk management tools, PU Prime is a platform suited to traders exploring strategies like pair trading.
Before placing a trade, users should always verify asset availability and ensure that their strategy aligns with the platform’s product offering.
Interactive Brokers is known for its broad market access and advanced functionality, including correlation tracking and the ability to run custom scripts.
It is often used by experienced traders who require more granular control over their trades and portfolio exposure.
TradingView is a charting and analysis platform that supports custom indicators and community-developed tools.
While it does not offer direct trade execution, it provides strong visualisation features for analysing price relationships between correlated assets.
Many traders use TradingView alongside their brokerage platform to plan and test pair trading ideas.
Key Takeaways
Platforms should offer charting tools, custom indicators, and stable execution for effective pair trading.
PU Prime supports MT4, MT5, and its own app, offering tools suited for correlation-based strategies.
Always check product availability before entering a trade.
TradingView and Interactive Brokers are also widely used for analysis and execution.
While pair trading offers potential advantages, it also comes with limitations that can affect its effectiveness.
Understanding these factors is vital for managing expectations and reducing risk.
Asset correlations are not fixed.
Even if two instruments have historically shown strong alignment, sudden changes in fundamentals, news events, or broader economic shifts can cause them to decouple.
Traders should monitor correlations over time and regularly re-evaluate asset pairs to confirm their ongoing suitability.
Pair trading depends on relative price movements between two assets.
During periods of low market volatility, spreads may remain stable or move within narrow ranges, reducing the number of viable trade setups.
In such conditions, traders may need to adjust their strategy or temporarily shift focus to more active markets.
Historical data plays a key role in pair selection and setup.
However, past performance is not always indicative of future behaviour.
As economic regimes, sector trends, and market dynamics evolve, they can weaken previously strong correlations.
To improve decision-making, traders should combine historical analysis with real-time data and a clear understanding of market context.
Key Takeaways
Correlated assets can decouple unexpectedly due to external events.
Low-volatility conditions may limit trading opportunities.
Historical relationships can change over time, so strategies should remain flexible.
Ongoing analysis is needed to maintain the strategy’s effectiveness.
Pair trading is a market-neutral strategy that focuses on the relative movement between two correlated assets.
By taking simultaneous long and short positions, traders aim to capitalise on price divergences while managing exposure to overall market trends.
For those new to pair trading, a demo account can be a valuable tool for testing strategies and building confidence.
It allows traders to practise identifying asset pairs, analysing correlations, and executing trades in a simulated environment without risking real capital.
Pair trading requires research, discipline, and regular evaluation.
While no strategy eliminates risk, combining thoughtful analysis with careful execution can support more consistent decision-making over time.
Traders interested in exploring this strategy can open a PU Prime demo account to practise in real market conditions.
Traders ready to engage with real markets can also open a free PU Prime live trading account to access a broad range of instruments across supported platforms.
The goal of pair trading is to profit from temporary price divergences between two historically correlated assets.
Traders take opposing positions in each asset and aim to benefit when the price relationship returns to its historical average.
Pair trading can be suitable for beginners who are comfortable with analysing data and monitoring positions closely.
Practising with a demo account is a helpful way to learn the strategy without risking real capital.
Pair trading is designed to be market-neutral, meaning it can be used in trending or range-bound markets.
However, its effectiveness depends on the strength and stability of the correlation between the assets involved.
Yes. PU Prime offers access to MT4, MT5, WebTrader, and its proprietary mobile app, all of which support tools for monitoring correlations and managing trades.
Asset availability may vary, so it’s important to confirm whether your selected instruments are supported.
Risks include false or shifting correlations, price divergence that does not revert, and overexposure to a single sector.
As with any strategy, ongoing analysis and risk management are essential.
Step into the world of trading with confidence today. Open a free PU Prime live CFD trading account now to experience real-time market action, or refine your strategies risk-free with our demo account.
This content is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without considering any individual investment objectives, financial situations. Any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or investment product are not indicative of future results.
PU Prime makes no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of this content and accepts no liability for any loss or damage arising from reliance on the information provided. Trading involves risk, and you should carefully consider your investment objectives and risk tolerance before making any trading decisions. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.

Trade forex, indices, metal, and more at industry-low spreads and lightning-fast execution.
Sign up for a PU Prime Live Account with our hassle-free process.
Effortlessly fund your account with a wide range of channels and accepted currencies.
Access hundreds of instruments under market-leading trading conditions.

Please note the Website is intended for individuals residing in jurisdictions where accessing the Website is permitted by law.
Please note that PU Prime and its affiliated entities are neither established nor operating in your home jurisdiction.
By clicking the "Acknowledge" button, you confirm that you are entering this website solely based on your initiative and not as a result of any specific marketing outreach. You wish to obtain information from this website which is provided on reverse solicitation in accordance with the laws of your home jurisdiction.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!
Ten en cuenta que el sitio web está destinado a personas que residen en jurisdicciones donde el acceso al sitio web está permitido por la ley.
Ten en cuenta que PU Prime y sus entidades afiliadas no están establecidas ni operan en tu jurisdicción de origen.
Al hacer clic en el botón "Aceptar", confirmas que estás ingresando a este sitio web por tu propia iniciativa y no como resultado de ningún esfuerzo de marketing específico. Deseas obtener información de este sitio web que se proporciona mediante solicitud inversa de acuerdo con las leyes de tu jurisdicción de origen.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!