-
- Trading Platforms
- PU Prime App
- MetaTrader 5
- MetaTrader 4
- PU Copy Trading
- Web Trader
- PU Social
-
- Trading Conditions
- Account Types
- Spreads, Costs & Swaps
- Deposits & Withdrawals
- Fee & Charges
- Trading Hours

Canadian government bond yields are a leading signal for moves in the Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) and the Canadian dollar (CAD). Watching the 2-year and 10-year benchmarks, the shape of the yield curve, and the Canada–US yield spread helps frame expectations for Bank of Canada policy, equity valuations, and currency flows. Traders who want to express a view on interest rates can use bond CFDs on PU Prime, noting that CFDs are leveraged derivatives and do not confer ownership.
The Canadian government bond market plays a powerful role in shaping the country’s financial landscape. While often less visible than equities or currencies, bond yields provide early signals of future movements in the S&P/TSX Composite Index and the Canadian dollar (CAD). These signals reflect shifting expectations around inflation, interest rates, and economic growth, all of which influence asset pricing across major markets.
Movements in bond yields are closely tied to anticipated changes in the Bank of Canada’s monetary policy. When yields rise or fall, they represent how the market is pricing in potential interest rate adjustments. These changes can drive capital flows, affect corporate borrowing conditions, and shape investor sentiment in both currency and equity markets.
Recognizing patterns in bond market behaviour can help traders and investors identify turning points in broader market conditions. Bond yields often act as a leading indicator, offering insight into how economic trends may unfold and where opportunities may emerge across Canadian financial assets.
In the Canadian bond market, yields and prices move in opposite directions. When a bond’s price rises, its yield falls. When the price drops, the yield rises. This principle is essential for interpreting how the market reacts to changes in interest rate expectations.
As an example, a 10-year Government of Canada bond with a face value of CAD 1,000 and a fixed annual coupon of 3 percent, yields 3 percent if purchased at par. If the price of that bond falls to CAD 950, its yield increases above 3 percent. If the price rises to CAD 1,050, the yield decreases below 3 percent.
Even though the bond always pays $30 per year, how much you pay for it changes what that $30 is worth to you. This difference in value explains why yields move in the opposite direction to prices, and why investors closely watch bond price shifts as interest rate expectations evolve.
These shifts reflect how the market values existing bonds compared to newer ones that may offer more attractive or less attractive returns based on expected rate changes.
| Scenario | Bond Price (CAD) | Annual Coupon (3%) | Yield (%) |
| Discount (Below Par) | 950 | 30 CAD | 3.16% |
| At Par | 1000 | 30 CAD | 3.00% |
| Premium (Above Par) | 1050 | 30 CAD | 2.86% |
(Yield = (Coupon ÷ Price) × 100)
The 2-year and 10-year Government of Canada bond yields are widely followed indicators. The 2-year yield responds to short-term developments and is often influenced by market expectations for upcoming Bank of Canada rate decisions. The 10-year yield provides insight into longer-term expectations about growth, inflation, and economic stability.
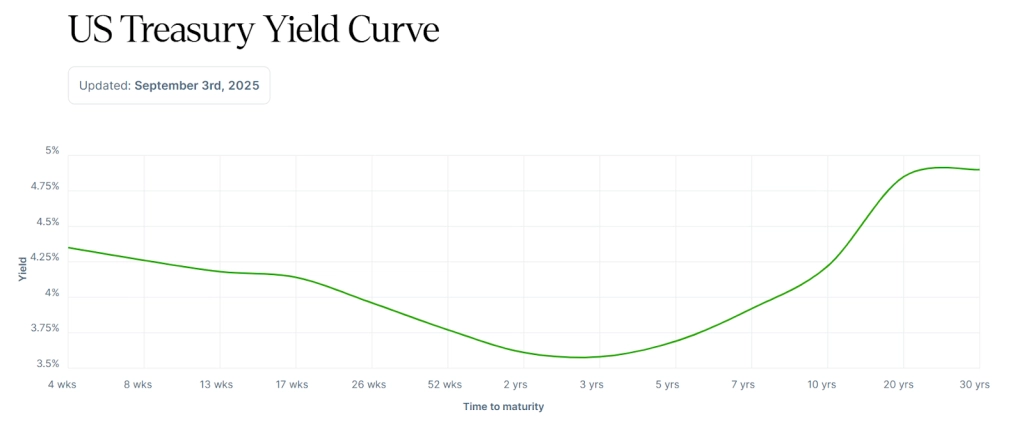
The yield curve illustrates the difference between yields on short-term and long-term bonds. When the 10-year yield is higher than the 2-year, the curve is considered steep. This typically reflects optimism about future growth. When the 2-year yield exceeds the 10-year, the curve becomes inverted. An inverted yield curve can suggest weakening economic momentum or a downturn. These curve shapes are closely monitored by analysts and policymakers.
Bond prices are sensitive to interest rate movements. When yields rise, the value of existing bonds falls, creating potential losses for holders. When yields decline, bond prices rise. These changes influence investment decisions across asset classes and can lead to adjustments in equity and currency markets as investors seek to manage risk and reallocate capital.
Key Takeaways
Bond prices and yields always move in opposite directions. The 2-year yield signals short-term interest rate expectations, while the 10-year reflects long-term views. The yield curve helps identify market expectations about future economic conditions. Shifts in yields impact bond values and influence broader asset pricing across markets.
Canadian government bond yields act as a live barometer of market expectations for future monetary policy. As new economic data is released or geopolitical events unfold, yields adjust quickly to reflect anticipated actions by the Bank of Canada. A sudden rise in yields, for example, may indicate the market is pricing in the likelihood of an interest rate hike. A drop in yields can signal expectations of rate cuts or a more accommodative policy stance.
Several core factors drive fluctuations in Canadian bond yields:
The Bank of Canada often communicates its policy outlook through forward guidance, offering signals on its likely future moves. Bond markets incorporate these signals almost immediately. If the Bank hints at holding rates steady, yields may stabilize. If it suggests tightening or easing is ahead, yields typically adjust to reflect that path before any actual rate change takes place.
One of the most watched signals in the bond market is the shape of the yield curve. When the spread between the 10-year and 2-year bond yields widens, it indicates steepening. This is often interpreted as a sign that the Bank of Canada may begin easing short-term rates while long-term inflation or growth expectations remain elevated. A steepening curve can suggest that monetary policy is shifting in response to slowing conditions or evolving risk outlooks.
As at 16 July 2025, the Department of Finance projected aggregate borrowing of C$623 billion for FY2025–26, including C$612 billion in Canadian-dollar issuance. *See Debt Management Strategy 2025–26 and the official PDF for details
This increased supply of long-term bonds can place upward pressure on yields even as the Bank of Canada lowers short-term rates. The bond market responds to both monetary and fiscal dynamics, which often pull in different directions.
Key Takeaways
Bond yields reflect market expectations of Bank of Canada rate moves and adjust faster than policy decisions. Inflation, economic data, and government policy are key drivers of yield movement. Forward guidance from the central bank shapes yield trends before rate changes occur. A steepening yield curve can indicate easing policy ahead, while large-scale bond issuance may lift long-term yields independently of short-term rates.
Canadian bond yields play a key role in determining the direction of the Canadian dollar (CAD). When yields on Canadian government bonds rise, they can attract foreign capital from investors seeking higher returns. Increased demand for Canadian assets leads to higher demand for the CAD, which supports or strengthens its value in global currency markets.
Traders closely monitor the yield spread between Canadian and United States government bonds. The difference between the 10-year yields in each country is especially important. A narrowing negative spread, where Canadian yields move closer to or above U.S. yields, can lift the CAD by making Canadian fixed income assets more appealing. A widening spread in favor of the U.S. tends to put downward pressure on the Canadian dollar.
By 15 July 2025, the Canada–US 10-year yield spread had narrowed to a nine-month low, according to Reuters, reflecting shifting policy expectations.
Foreign investors, central banks, pension funds, and mutual funds all allocate capital based on relative yield opportunities. When Canadian yields become more competitive, international funds may increase their exposure to Canadian government bonds. This increased investment creates demand for Canadian dollars, supporting the exchange rate and improving liquidity in bond and currency markets.
Large institutional investors often adjust positions in both bond and currency markets at once. If Canadian yields appear more attractive on a risk-adjusted basis, institutions may rebalance portfolios to include more Canadian debt, increasing demand for both bonds and CAD. This activity can reduce volatility and promote more stable trading conditions, especially during periods of policy clarity or consistent economic performance.
Key Takeaways
Rising Canadian bond yields can increase demand for the CAD by attracting global investors. Yield spreads between Canadian and U.S. bonds are a major factor in USD/CAD exchange rate movements. A narrowing yield gap supports CAD strength, while a widening gap favors USD outperformance. Capital flows from institutional investors and central banks reinforce the bond-yield-to-currency connection.
Bond yields influence equity markets through several channels, especially in economies like Canada where interest-sensitive sectors hold significant weight in major indices. When yields rise, borrowing costs increase for businesses. Higher financing costs can limit investment, reduce profit margins, and lead to more cautious spending. These pressures can negatively affect company earnings, particularly for firms that rely heavily on credit.
Rising yields also affect how investors value stocks. In discounted cash flow (DCF) models, higher interest rates increase the discount rate applied to future earnings. This reduces the present value of those earnings and can lead to lower stock prices. Sectors such as technology and real estate, which are valued based on longer-term growth, tend to be more sensitive to these changes in interest rate conditions.
When the Bank of Canada lowers interest rates, bond yields often decline. Lower yields reduce borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, which can improve corporate performance and stimulate economic activity. In turn, this creates a more favourable environment for equities. Investors may also shift capital out of lower-yielding bonds and into stocks, supporting market gains.
The relationship between bond yields and stock performance varies across sectors. Financial institutions, particularly banks, may benefit from a steepening yield curve as it improves the spread between their lending and deposit rates. In contrast, sectors like utilities and real estate, which tend to carry high debt loads and operate in regulated environments, can face pressure when yields rise.
Sharp changes in bond yields can act as a signal for volatility in equity markets. If yields rise rapidly due to unexpected inflation or shifts in central bank policy, equity markets may react with increased uncertainty. Investors often interpret bond market turbulence as a warning sign of changing economic conditions that could influence corporate performance.
Key Takeaways
Bond yields influence borrowing costs, profit outlooks, and equity market sentiment. Higher yields can reduce stock valuations by increasing discount rates. Sectors respond differently to yield changes, with banks often gaining and utilities under pressure. Rapid shifts in yields may signal upcoming volatility in Canadian equity markets, including the TSX.
A Contract for Difference (CFD) allows traders to speculate on the price movements of a financial instrument without owning the underlying asset. In the case of a bond CFD, traders can take positions based on their expectations of how interest rates and yields will move. These contracts reflect the value of the underlying bond and allow for long or short positions depending on market outlook.
Bond CFDs offer a way to express a directional view on interest rates. For example, if a trader believes that bond yields will rise due to potential Bank of Canada tightening, they may short a bond CFD in expectation that bond prices will fall. If they expect yields to decline following soft economic data or a policy shift, they may go long, anticipating prices will rise.
Bonds with longer maturities, such as the 10-year benchmark, are commonly used by traders to assess market sentiment around growth, inflation, and central bank direction. Using CFDs linked to these instruments allows for flexible positioning in response to evolving macroeconomic signals.
PU Prime offers a selection of bond CFDs, providing traders with the ability to act on interest rate movements and policy expectations. These tools are designed for speculation and short-term positioning. Traders can use them alongside economic releases, policy announcements, and bond market trends to build strategies tailored to shifting market conditions.
It is important to understand that trading CFDs involves leverage, which magnifies both potential gains and losses. These products do not involve ownership of the actual government bond. Instead, traders are exposed to the price changes of the bond over time. Volatility, liquidity conditions, and economic surprises can all increase trading risk.
Bond CFDs provide real-time exposure to interest rate sentiment, the flexibility to go long or short, and the ability to react quickly to market developments. However, they also carry risks tied to leverage, price gaps, and derivative complexity. A clear understanding of bond market mechanics is essential for effective use of these products.
Key Takeaways
Bond CFDs allow traders to speculate on bond price movements without owning the bond. Traders use them to express views on interest rate direction based on macroeconomic expectations. PU Prime offers access to global bond CFDs through futures in its trading platform. CFDs carry leverage and risk, making them suitable for informed, risk-managed strategies.
Canadian bond yields offer timely insight into future moves in interest rates, equity performance, and currency trends. For traders, following these signals can lead to better-informed decisions across multiple markets.
By reading shifts in yield levels, curve shape, and cross-border spreads, traders can anticipate economic momentum and market reactions with greater clarity.
Turn economic signals into trading opportunities. With flexible tools and deep market coverage, PU Prime helps you stay one step ahead. Access Canada 10-Year Government Bond CFDs on PU Prime and start trading with insights shaped by market signals. Stay informed, stay ready, and take control of your strategy.
Bond yields reflect what the market expects the Bank of Canada to do with interest rates. If yields rise, it often signals that traders are anticipating future rate hikes. If yields fall, the market may be pricing in potential rate cuts or slower economic growth.
When Canadian bond yields rise relative to other countries, such as the United States, they can attract foreign investment. This demand for Canadian assets increases demand for the CAD, which may strengthen the currency.
Higher bond yields raise borrowing costs for businesses and reduce the present value of future earnings. This can lead to lower stock valuations, especially in sectors that are sensitive to interest rates.
It is a financial derivative that allows traders to speculate on the price movements of the Canadian 10-year government bond. Traders do not own the bond itself. Instead, they take positions based on whether they expect bond prices to rise or fall.
An inverted curve, where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields, can indicate market expectations of slowing growth or potential recession. It has historically been viewed as a warning signal for economic downturns.
Traders can use the shape and movement of the yield curve to anticipate interest rate policy shifts and sector rotations. A steepening curve may benefit banks and cyclicals, while an inverted curve can increase caution around growth-sensitive assets.
Step into the world of trading with confidence today. Open a free PU Prime live CFD trading account now to experience real-time market action, or refine your strategies risk-free with our demo account.
This content is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice, a personal recommendation, or an offer to buy or sell any financial instruments.
This material has been prepared without considering any individual investment objectives, financial situations. Any references to past performance of a financial instrument, index, or investment product are not indicative of future results.
PU Prime makes no representation as to the accuracy or completeness of this content and accepts no liability for any loss or damage arising from reliance on the information provided. Trading involves risk, and you should carefully consider your investment objectives and risk tolerance before making any trading decisions. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.

Trade forex, indices, metal, and more at industry-low spreads and lightning-fast execution.
Sign up for a PU Prime Live Account with our hassle-free process.
Effortlessly fund your account with a wide range of channels and accepted currencies.
Access hundreds of instruments under market-leading trading conditions.

Please note the Website is intended for individuals residing in jurisdictions where accessing the Website is permitted by law.
Please note that PU Prime and its affiliated entities are neither established nor operating in your home jurisdiction.
By clicking the "Acknowledge" button, you confirm that you are entering this website solely based on your initiative and not as a result of any specific marketing outreach. You wish to obtain information from this website which is provided on reverse solicitation in accordance with the laws of your home jurisdiction.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!
Ten en cuenta que el sitio web está destinado a personas que residen en jurisdicciones donde el acceso al sitio web está permitido por la ley.
Ten en cuenta que PU Prime y sus entidades afiliadas no están establecidas ni operan en tu jurisdicción de origen.
Al hacer clic en el botón "Aceptar", confirmas que estás ingresando a este sitio web por tu propia iniciativa y no como resultado de ningún esfuerzo de marketing específico. Deseas obtener información de este sitio web que se proporciona mediante solicitud inversa de acuerdo con las leyes de tu jurisdicción de origen.
Thank You for Your Acknowledgement!